In today’s digital age, nearly everyone is online. With billions of searches conducted daily, businesses…
What is an SSL Certificate?
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, security has become a paramount concern for websites and their users. One crucial tool in safeguarding online interactions is the SSL certificate. But what is an SSL certificate? This blog post aims to answer this question in detail, exploring the concept, importance, types, and implementation of SSL certificates to help you understand why they are vital for your online presence.
Understanding the Basics: What is an SSL Certificate?
To answer the question, “What is an SSL certificate?” we need to start with the fundamentals of how data is transmitted over the internet. When you visit a website, data is exchanged between your browser and the web server hosting the site. This data can include sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, and personal details. Without proper encryption, this data can be intercepted by malicious actors, leading to potential data breaches and identity theft.
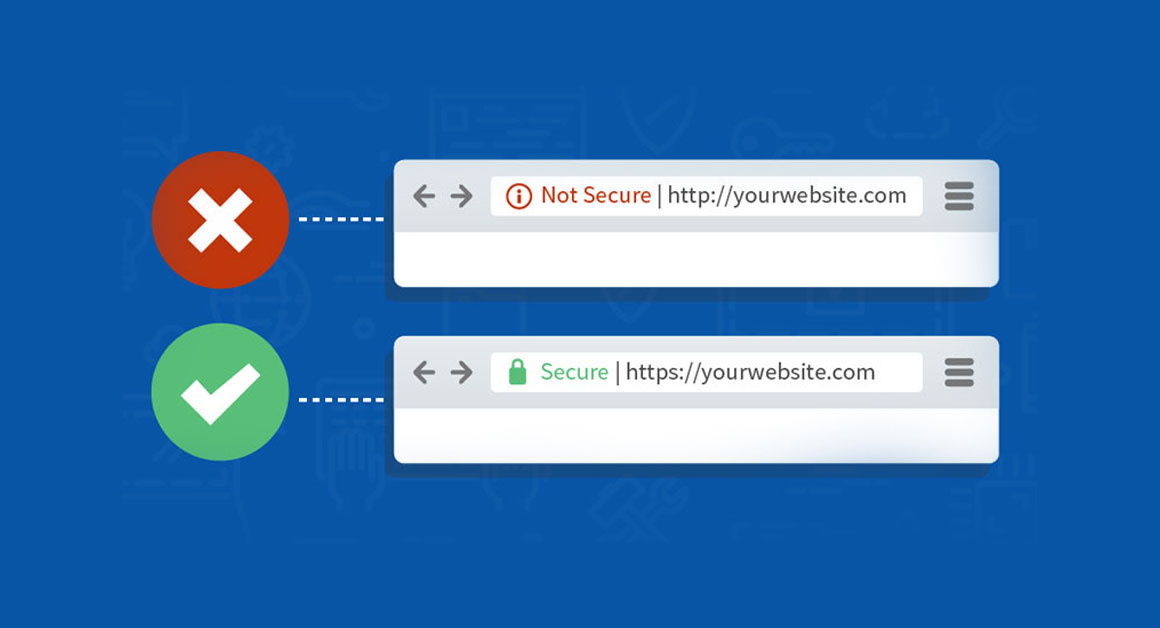
An SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a digital certificate that establishes a secure, encrypted connection between a user’s browser and a web server. This encryption ensures that any data exchanged between the browser and server remains private and secure. When a website has an SSL certificate, it uses the HTTPS protocol (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) instead of the standard HTTP, signaling to users that the site is secure.
The Importance of SSL Certificates
Understanding “what is an SSL certificate” also involves recognizing its significance. Here are several key reasons why SSL certificates are essential for any website:
Data Encryption
The primary purpose of an SSL certificate is to encrypt data transmitted between a user’s browser and a web server. This encryption converts the data into a coded form that can only be deciphered by the intended recipient. This ensures that sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card details, remains secure from eavesdroppers and hackers.
Authentication and Trust
SSL certificates also provide authentication, verifying the identity of the website owner. This process involves a third-party Certificate Authority (CA) that validates the website’s identity before issuing the certificate. When users see the padlock icon in their browser’s address bar, they can trust that the website is legitimate and their data is safe.
SEO Benefits
Search engines like Google prioritize secure websites in their search results. Websites with SSL certificates are more likely to rank higher than those without. This SEO benefit can lead to increased traffic and visibility for your site, making SSL certificates an essential component of any SEO strategy.
Compliance with Regulations
Many data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), require websites to implement SSL encryption to protect user data. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines and legal consequences.
Enhanced User Experience
A secure website provides a better user experience by instilling confidence in visitors. When users see the HTTPS and padlock symbol, they know their information is safe, which can lead to higher engagement, longer visit durations, and increased conversions.
Types of SSL Certificates
There are several types of SSL certificates available, each offering different levels of validation and security. Understanding these types will help you choose the right certificate for your website.
Domain Validation (DV) SSL Certificates
Domain Validation SSL certificates are the most basic type of SSL certificate. They verify that the domain owner has control over the domain but do not conduct any additional validation. DV certificates are typically issued quickly and are suitable for small websites and blogs.
Advantages of DV SSL Certificates:
- Fast and easy to obtain
- Affordable
- Provides basic encryption
Disadvantages of DV SSL Certificates:
- Limited validation and trust
- Not suitable for e-commerce or business websites
Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificates
Organization Validation SSL certificates provide a higher level of validation than DV certificates. In addition to verifying domain ownership, the Certificate Authority (CA) also validates the organization’s identity by checking business registration documents. OV certificates are suitable for business websites and e-commerce platforms.
Advantages of OV SSL Certificates:
- Higher level of trust and validation
- Displays organization details in the certificate
- Suitable for businesses and e-commerce
Disadvantages of OV SSL Certificates:
- Longer issuance time
- Higher cost than DV certificates
Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates
Extended Validation SSL certificates offer the highest level of validation and trust. The CA conducts a thorough vetting process, including verifying the organization’s legal existence, operational status, and physical location. Websites with EV certificates display a green address bar or the organization’s name in the browser, providing maximum trust to users.
Advantages of EV SSL Certificates:
- Highest level of trust and validation
- Green address bar with the organization’s name
- Ideal for e-commerce and high-profile websites
Disadvantages of EV SSL Certificates:
- Lengthy and rigorous validation process
- Most expensive type of SSL certificate
Wildcard SSL Certificates
Wildcard SSL certificates allow you to secure a primary domain and an unlimited number of subdomains with a single certificate. For example, a wildcard SSL certificate for *.example.com would cover www.example.com, blog.example.com, shop.example.com, and any other subdomains.
Advantages of Wildcard SSL Certificates:
- Cost-effective for multiple subdomains
- Simplifies certificate management
- Provides the same level of encryption as other SSL certificates
Disadvantages of Wildcard SSL Certificates:
- More expensive than single-domain certificates
- Some CAs do not offer EV wildcard certificates
Multi-Domain SSL Certificates
Multi-Domain SSL certificates, also known as Subject Alternative Name (SAN) certificates, allow you to secure multiple domains with a single certificate. This is useful for organizations managing multiple websites or brands.
Advantages of Multi-Domain SSL Certificates:
- Cost-effective for multiple domains
- Simplifies certificate management
- Supports various validation levels (DV, OV, EV)
Disadvantages of Multi-Domain SSL Certificates:
- More expensive than single-domain certificates
- Complex management if domains are not related
How SSL Certificates Work
To understand “what is an SSL certificate,” it’s essential to know how they work to secure data transmission. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
- SSL Handshake: When a user visits a website with an SSL certificate, their browser and the web server initiate an SSL handshake. This process involves the browser and server exchanging cryptographic keys and establishing a secure connection.
- Public and Private Keys: During the SSL handshake, the server presents its SSL certificate, which contains a public key. The browser generates a session key, encrypts it with the server’s public key, and sends it back to the server. The server then decrypts the session key using its private key.
- Session Key: Once the session key is established, both the browser and server use it to encrypt and decrypt data exchanged during the session. This ensures that any data transmitted is secure and cannot be intercepted by third parties.
- Secure Connection: With the session key in place, the browser and server establish a secure, encrypted connection. The browser displays the HTTPS protocol and a padlock icon, indicating that the connection is secure.
Implementing SSL Certificates
Implementing SSL certificates on your website involves several steps. Here’s a guide to help you through the process:
Purchase an SSL Certificate
Choose the type of SSL certificate that suits your website’s needs and purchase it from a reputable Certificate Authority (CA) or a trusted web hosting provider.
Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
A Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is a file that contains your website’s information and public key. You can generate a CSR through your web hosting control panel or server’s command line interface.
Submit the CSR to the CA
Submit the CSR to the Certificate Authority (CA) for validation. The CA will verify your information and issue the SSL certificate if everything checks out.
Install the SSL Certificate
Once you receive the SSL certificate, you need to install it on your web server. This process varies depending on your hosting provider and server type. Most hosting providers offer detailed instructions or support to help you with installation.
Update Your Website to Use HTTPS
After installing the SSL certificate, update your website’s URLs to use the HTTPS protocol. This involves changing internal links, updating scripts and resources, and configuring any third-party services to use HTTPS.
Test Your SSL Certificate
Use online tools like SSL Labs’ SSL Test to check the installation and configuration of your SSL certificate. Ensure there are no issues and that your website is fully secure.
Common SSL Certificate Errors and Solutions
While implementing SSL certificates, you may encounter some common errors. Here are a few examples and their solutions:
Mixed Content
Mixed content occurs when a secure HTTPS page includes resources (such as images, scripts, or stylesheets) loaded over an insecure HTTP connection. This can compromise the security of your website.
Solution: Update all internal links and resources to use HTTPS. Use online tools to scan your website for mixed content and fix any issues.
Expired SSL Certificate
SSL certificates have an expiration date and must be renewed periodically. An expired certificate will result in browser warnings and may deter users from visiting your site.
Solution: Set up automatic renewal with your CA or hosting provider. Monitor your certificate’s expiration date and renew it before it expires.
Certificate Name Mismatch
This error occurs when the domain name in the SSL certificate does not match the domain name in the browser’s address bar. It can happen if you’ve changed your domain name or if there’s a typo in the certificate.
Solution: Ensure the domain name in your SSL certificate matches your website’s domain. If you’ve changed your domain, obtain a new SSL certificate with the correct name.
Conclusion
In the digital age, understanding “what is an SSL certificate” is crucial for anyone looking to establish a secure online presence. An SSL certificate not only encrypts data transmitted between a user’s browser and a web server but also provides authentication, enhances trust, and improves SEO rankings. Whether you’re running a small blog, an e-commerce site, or a large business website, implementing an SSL certificate is essential to protect your users’ data and ensure compliance with regulations.
By choosing the right type of SSL certificate, following best practices for implementation, and addressing common errors, you can create a secure and trustworthy online environment for your visitors. So, the next time someone asks, “What is an SSL certificate?” you can confidently explain its importance and the role it plays in safeguarding digital interactions.